HRNet-OCR的原代码将各种超参数和训练超参数冗杂在一起,导致不用于其他数据集会很不方便,为了方便调用模型,对模型的超参进行抽离后得到简易版模型实现。
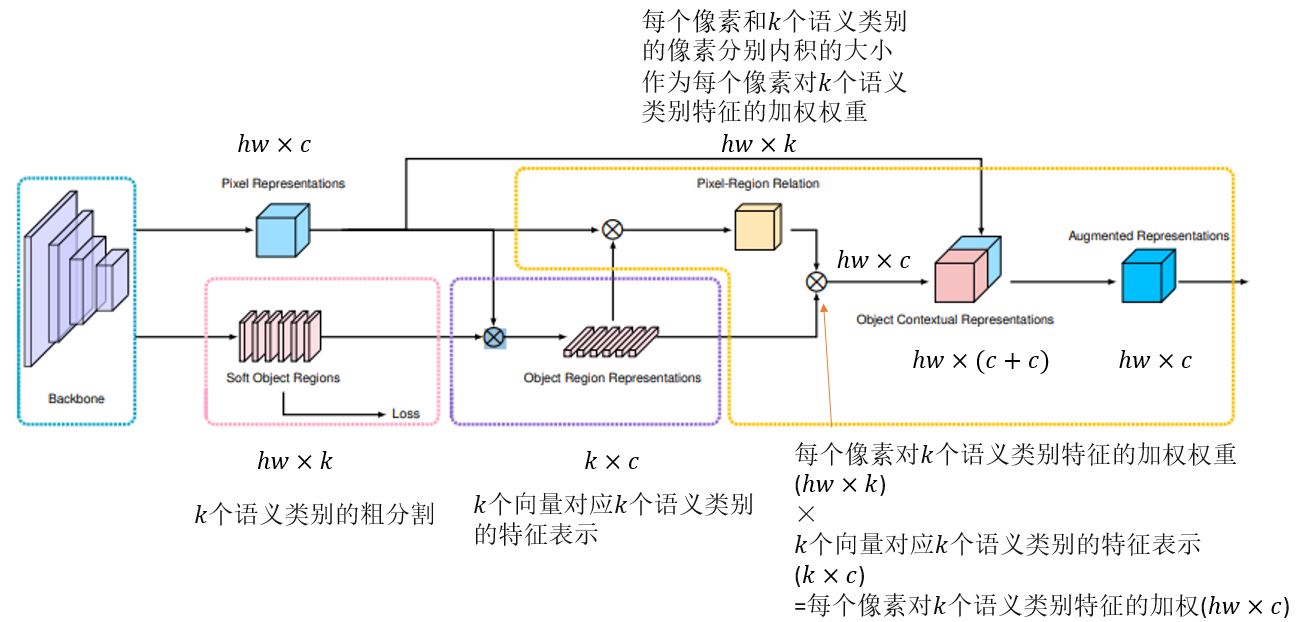
OCR如下图
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Copyright (c) Microsoft
# Licensed under the MIT License.
# Written by Ke Sun (sunk@mail.ustc.edu.cn), Jingyi Xie (hsfzxjy@gmail.com)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import logging
import functools
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch._utils
import torch.nn.functional as F
# from .bn_helper import BatchNorm2d, BatchNorm2d_class, relu_inplace
# from bn_helper import BatchNorm2d, BatchNorm2d_class, relu_inplace
BatchNorm2d_class = BatchNorm2d = nn.BatchNorm2d
relu_inplace = True
ALIGN_CORNERS = True
BN_MOMENTUM = 0.1
# logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class ModuleHelper:
@staticmethod
def BNReLU(num_features, bn_type=None, **kwargs):
return nn.Sequential(
BatchNorm2d(num_features, **kwargs),
nn.ReLU()
)
@staticmethod
def BatchNorm2d(*args, **kwargs):
return BatchNorm2d
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=False)
class SpatialGather_Module(nn.Module):
"""
Aggregate the context features according to the initial
predicted probability distribution.
Employ the soft-weighted method to aggregate the context.
"""
def __init__(self, cls_num=0, scale=1):
super(SpatialGather_Module, self).__init__()
self.cls_num = cls_num
self.scale = scale
def forward(self, feats, probs):
batch_size, c, h, w = probs.size(0), probs.size(1), probs.size(2), probs.size(3)
probs = probs.view(batch_size, c, -1)
feats = feats.view(batch_size, feats.size(1), -1)
feats = feats.permute(0, 2, 1) # batch x hw x c
probs = F.softmax(self.scale * probs, dim=2)# batch x k x hw
ocr_context = torch.matmul(probs, feats)\
.permute(0, 2, 1).unsqueeze(3)# batch x k x c
return ocr_context
class _ObjectAttentionBlock(nn.Module):
'''
The basic implementation for object context block
Input:
N X C X H X W
Parameters:
in_channels : the dimension of the input feature map
key_channels : the dimension after the key/query transform
scale : choose the scale to downsample the input feature maps (save memory cost)
bn_type : specify the bn type
Return:
N X C X H X W
'''
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
key_channels,
scale=1,
bn_type=None):
super(_ObjectAttentionBlock, self).__init__()
self.scale = scale
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.key_channels = key_channels
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=(scale, scale))
self.f_pixel = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.key_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
ModuleHelper.BNReLU(self.key_channels, bn_type=bn_type),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.key_channels, out_channels=self.key_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
ModuleHelper.BNReLU(self.key_channels, bn_type=bn_type),
)
self.f_object = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.key_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
ModuleHelper.BNReLU(self.key_channels, bn_type=bn_type),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.key_channels, out_channels=self.key_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
ModuleHelper.BNReLU(self.key_channels, bn_type=bn_type),
)
self.f_down = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.in_channels, out_channels=self.key_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
ModuleHelper.BNReLU(self.key_channels, bn_type=bn_type),
)
self.f_up = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.key_channels, out_channels=self.in_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
ModuleHelper.BNReLU(self.in_channels, bn_type=bn_type),
)
def forward(self, x, proxy):
batch_size, h, w = x.size(0), x.size(2), x.size(3)
if self.scale > 1:
x = self.pool(x)
query = self.f_pixel(x).view(batch_size, self.key_channels, -1)
query = query.permute(0, 2, 1)
key = self.f_object(proxy).view(batch_size, self.key_channels, -1)
value = self.f_down(proxy).view(batch_size, self.key_channels, -1)
value = value.permute(0, 2, 1)
sim_map = torch.matmul(query, key)
sim_map = (self.key_channels**-.5) * sim_map
sim_map = F.softmax(sim_map, dim=-1)
# add bg context ...
context = torch.matmul(sim_map, value)
context = context.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous()
context = context.view(batch_size, self.key_channels, *x.size()[2:])
context = self.f_up(context)
if self.scale > 1:
context = F.interpolate(input=context, size=(h, w), mode='nearest')#, align_corners=ALIGN_CORNERS)
return context
class ObjectAttentionBlock2D(_ObjectAttentionBlock):
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
key_channels,
scale=1,
bn_type=None):
super(ObjectAttentionBlock2D, self).__init__(in_channels,
key_channels,
scale,
bn_type=bn_type)
class SpatialOCR_Module(nn.Module):
"""
Implementation of the OCR module:
We aggregate the global object representation to update the representation for each pixel.
"""
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
key_channels,
out_channels,
scale=1,
dropout=0.1,
bn_type=None):
super(SpatialOCR_Module, self).__init__()
self.object_context_block = ObjectAttentionBlock2D(in_channels,
key_channels,
scale,
bn_type)
_in_channels = 2 * in_channels
self.conv_bn_dropout = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(_in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, padding=0, bias=False),
ModuleHelper.BNReLU(out_channels, bn_type=bn_type),
nn.Dropout2d(dropout)
)
def forward(self, feats, proxy_feats):
context = self.object_context_block(feats, proxy_feats)
output = self.conv_bn_dropout(torch.cat([context, feats], 1))
return output
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=relu_inplace)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out = out + residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = BatchNorm2d(planes, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * self.expansion, kernel_size=1,
bias=False)
self.bn3 = BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion,
momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=relu_inplace)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out = out + residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class HighResolutionModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_inchannels,
num_channels, fuse_method, multi_scale_output=True):
#2 BasicBlock [4,4] [48,96] [48,96] 'sum'
super(HighResolutionModule, self).__init__()
self._check_branches(
num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_inchannels, num_channels)
self.num_inchannels = num_inchannels
self.fuse_method = fuse_method
self.num_branches = num_branches
self.multi_scale_output = multi_scale_output
self.branches = self._make_branches(#2 BasicBlock [4,4] [48,96]
num_branches, blocks, num_blocks, num_channels)
self.fuse_layers = self._make_fuse_layers()
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=relu_inplace)
def _check_branches(self, num_branches, blocks, num_blocks,
num_inchannels, num_channels):
if num_branches != len(num_blocks):
error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_BLOCKS({})'.format(
num_branches, len(num_blocks))
logger.error(error_msg)
raise ValueError(error_msg)
if num_branches != len(num_channels):
error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_CHANNELS({})'.format(
num_branches, len(num_channels))
logger.error(error_msg)
raise ValueError(error_msg)
if num_branches != len(num_inchannels):
error_msg = 'NUM_BRANCHES({}) <> NUM_INCHANNELS({})'.format(
num_branches, len(num_inchannels))
logger.error(error_msg)
raise ValueError(error_msg)
def _make_one_branch(self, branch_index, block, num_blocks, num_channels,
stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or \
self.num_inchannels[branch_index] != num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(#如果输入通道数 和 扩展后的通道数不同 则卷积升通道
nn.Conv2d(self.num_inchannels[branch_index],
num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion,
momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
)
# num_blocks = [4,4]
# for i in range(1, num_blocks[branch_index]) = [0,1,2,3]
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.num_inchannels[branch_index],#[0]
num_channels[branch_index], stride, downsample))
self.num_inchannels[branch_index] = \
num_channels[branch_index] * block.expansion
for i in range(1, num_blocks[branch_index]):#[1,2,3]
layers.append(block(self.num_inchannels[branch_index],
num_channels[branch_index]))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _make_branches(self, num_branches, block, num_blocks, num_channels):
branches = []#2 BasicBlock [4,4] [48,96]
for i in range(num_branches):#for i in range(2) 第i个分支
branches.append(
self._make_one_branch(i, block, num_blocks, num_channels))
return nn.ModuleList(branches)
def _make_fuse_layers(self):
if self.num_branches == 1:
return None
num_branches = self.num_branches#2
num_inchannels = self.num_inchannels#[48,96]
#fuse_layers[i][j] 第i个分支融合第j个分支的操作
fuse_layers = []#二维数组 存num_branches个分支总的操作
#[[None,Conv1×1+上采样],[Conv3×3+下采样,None]]
for i in range(num_branches if self.multi_scale_output else 1):
#fuse_layer存第i个分支的操作 有
fuse_layer = []
for j in range(num_branches):
#如果当分支j大于分支i,则需要上采样先使用1x1卷积将j分支的通道数变得和i分支一致,进而跟着BN,
#然后依据上采样因子将j分支分辨率上采样到和i分支分辨率相同(F.interpolate(self.fuse_layers[i][j](x[j]))
if j > i:
fuse_layer.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_inchannels[j],
num_inchannels[i],
1,
1,
0,
bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(num_inchannels[i], momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)))
# 分支j==i不作操作
elif j == i:
fuse_layer.append(None)
# 分支j<分支i 则需要下采样j至分支i 直接使用步长为2的3x3卷积+relu 将j分支的通道数变得和i分支一致且分辨率下降为1/4
else:
conv3x3s = []
for k in range(i-j):#i=2 j=0 k==2-0-1=1 则不加relu
if k == i - j - 1:
num_outchannels_conv3x3 = num_inchannels[i]
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_inchannels[j],
num_outchannels_conv3x3,
3, 2, 1, bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(num_outchannels_conv3x3,
momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)))
else:#i=2 j=0 k!=2-0-1=1 则加relu
num_outchannels_conv3x3 = num_inchannels[j]
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(num_inchannels[j],
num_outchannels_conv3x3,
3, 2, 1, bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(num_outchannels_conv3x3,
momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=relu_inplace)))
fuse_layer.append(nn.Sequential(*conv3x3s))
fuse_layers.append(nn.ModuleList(fuse_layer))
return nn.ModuleList(fuse_layers)
def get_num_inchannels(self):
return self.num_inchannels
def forward(self, x):
#x表示每个分支输入的特征,如果有两个分支,则x就是一个二维数组,x[0]和x[1]就是两个输入分支的特征
#如果只有一个分支就直接返回,不做任何融合
if self.num_branches == 1:
return [self.branches[0](x[0])]
#有多个分支的时候,对每个分支都先用_make_branch函数生成主特征网络,再将特定的网络特征进行融合
for i in range(self.num_branches):
x[i] = self.branches[i](x[i])
#这里是利用融合模块进行特征融合
x_fuse = []
for i in range(len(self.fuse_layers)):
#对每个分支用_make_fuse_layer生成要进行融合操作的层
y = x[0] if i == 0 else self.fuse_layers[i][0](x[0])
# 进行特征融合,举个例子,运行到分支一的时候,self.fuse_layers[i][0](x[0])先生成对于分支一的融合操作
for j in range(1, self.num_branches):#for循环得到每个分支对于分支一的采样结果 当i=j,就是分支一本身不进行任何操作直接cat
# i<j的时候就是分支2对于分支1来说要进行上采样,然后cat得到结果,并cat得到最后的输出
if i == j:
y = y + x[j]
elif j > i:
width_output = x[i].shape[-1]
height_output = x[i].shape[-2]
y = y + F.interpolate(
self.fuse_layers[i][j](x[j]),
size=[height_output, width_output],
mode='nearest')#, align_corners=ALIGN_CORNERS)
# 分支j<分支i 则需要下采样j至分支i 直接使用步长为2的3x3卷积+relu 将j分支的通道数变得和i分支一致且分辨率下降为1/4
else:
y = y + self.fuse_layers[i][j](x[j])
x_fuse.append(self.relu(y))
return x_fuse
blocks_dict = {
'BASIC': BasicBlock,
'BOTTLENECK': Bottleneck
}
class hyper_parameters:
def __init__(self):
self.blocks = ['BOTTLENECK','BASIC','BASIC','BASIC']#[Bottleneck,BasicBlock, BasicBlock, BasicBlock]
self.num_modules = [1, 1, 4, 3]#modules重复数 [重复1次的4个Bottleneck,重复1次的1个BasicBlock,重复4次的1个BasicBlock,重复3次的1个BasicBlock]
self.num_branches = [1, 2, 3, 4]#分支数
self.num_blocks = [[4], [4, 4], [4, 4, 4], [4, 4, 4, 4]]
self.num_channels = [[64], [48, 96], [48, 96, 192], [48, 96, 192, 384]]#各条分支的通道数
self.fuse_method = ['sum', 'sum', 'sum', 'sum']
hp = hyper_parameters()
class HighResolutionNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, blocks=['BOTTLENECK','BASIC','BASIC','BASIC']
, num_channels=[[64], [48, 96], [48, 96, 192], [48, 96, 192, 384]]
, num_modules=[1, 1, 4, 3]
, num_branches=[1, 2, 3, 4]
, num_blocks=[[4], [4, 4], [4, 4, 4], [4, 4, 4, 4]]
, fuse_method=['sum', 'sum', 'sum', 'sum']):
global ALIGN_CORNERS
# extra = config.MODEL.EXTRA
super(HighResolutionNet, self).__init__()
ALIGN_CORNERS = True#config.MODEL.ALIGN_CORNERS
self.num_branches = num_branches
self.num_class = 12
# stem net
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = BatchNorm2d(64, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1,
bias=False)
self.bn2 = BatchNorm2d(64, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=relu_inplace)
num_channels1 = num_channels[0][0] # 64
block = blocks_dict[blocks[0]] # 'BOTTLENECK'
num_blocks1 = num_blocks[0][0] # 4
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_channels1,
num_blocks1) # 进入4个Bottleneck前通道数64和 出来的通道数num_channels
stage1_out_channel = block.expansion * num_channels1 # 4*[64]
# self.stage2_cfg = extra['STAGE2']
num_channels2 = num_channels[1]
block = blocks_dict[blocks[1]]
num_channels2 = [
num_channels2[i] * block.expansion for i in range(len(num_channels2))] # 1*[48,96]
self.transition1 = self._make_transition_layer( # [256]->[48,96]
[stage1_out_channel], num_channels2)
self.stage2, pre_stage_channels = self._make_stage(
num_channels2, num_modules[1], num_branches[1], num_blocks[1], num_channels[1], block,
fuse_method[1])
# self.stage3_cfg = extra['STAGE3']
num_channels3 = num_channels[2]
block = blocks_dict[blocks[2]]
num_channels3 = [
num_channels3[i] * block.expansion for i in range(len(num_channels3))]
self.transition2 = self._make_transition_layer(
pre_stage_channels, num_channels3)
self.stage3, pre_stage_channels = self._make_stage(
num_channels3, num_modules[2], num_branches[2], num_blocks[2], num_channels[2], block,
fuse_method[2])
# self.stage4_cfg = extra['STAGE4']
num_channels4 = num_channels[3]
block = blocks_dict[blocks[3]]
num_channels4 = [
num_channels4[i] * block.expansion for i in range(len(num_channels4))]
self.transition3 = self._make_transition_layer(
pre_stage_channels, num_channels4)
self.stage4, pre_stage_channels = self._make_stage(
num_channels4, num_modules[3], num_branches[3], num_blocks[3], num_channels[3], block,
fuse_method[3], multi_scale_output=True)
last_inp_channels = np.int(np.sum(pre_stage_channels))
ocr_mid_channels = 512 # config.MODEL.OCR.MID_CHANNELS
ocr_key_channels = 256 # config.MODEL.OCR.KEY_CHANNELS
self.conv3x3_ocr = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(last_inp_channels, ocr_mid_channels,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
BatchNorm2d(ocr_mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=relu_inplace),
)
self.ocr_gather_head = SpatialGather_Module(self.num_class) # config.DATASET.NUM_CLASSES
self.ocr_distri_head = SpatialOCR_Module(in_channels=ocr_mid_channels,
key_channels=ocr_key_channels,
out_channels=ocr_mid_channels,
scale=1,
dropout=0.05,
)
self.cls_head = nn.Conv2d(ocr_mid_channels, self.num_class, # config.DATASET.NUM_CLASSES
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
self.aux_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(last_inp_channels, last_inp_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0),
BatchNorm2d(last_inp_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=relu_inplace),
nn.Conv2d(last_inp_channels, self.num_class, # config.DATASET.NUM_CLASSES
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
)
def _make_transition_layer(
self, num_channels_pre_layer, num_channels_cur_layer):
num_branches_cur = len(num_channels_cur_layer)
num_branches_pre = len(num_channels_pre_layer)
transition_layers = []
for i in range(num_branches_cur): # [256]->[48,96]
if i < num_branches_pre: # 对所有前1项做升降维
if num_channels_cur_layer[i] != num_channels_pre_layer[i]: # 如果48!=256
transition_layers.append(nn.Sequential( # 256 -> 48
nn.Conv2d(num_channels_pre_layer[i],
num_channels_cur_layer[i],
3,
1,
1,
bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(
num_channels_cur_layer[i], momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=relu_inplace)))
else:
transition_layers.append(None)
else:
conv3x3s = []
for j in range(i + 1 - num_branches_pre): # 1>=1 for j in (1+1-1)
inchannels = num_channels_pre_layer[-1] # [256]
outchannels = num_channels_cur_layer[i] \
if j == i - num_branches_pre else inchannels # [48,96][1]=96 j=0==1-1=0
conv3x3s.append(nn.Sequential( # 加一个256->96的conv
nn.Conv2d(
inchannels, outchannels, 3, 2, 1, bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(outchannels, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
nn.ReLU(inplace=relu_inplace)))
transition_layers.append(nn.Sequential(*conv3x3s)) # 把多出来的操作组成一个序列加进transition_layers
return nn.ModuleList(transition_layers)
def _make_layer(self, block, inplanes, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion, momentum=BN_MOMENTUM),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _make_stage(self, num_inchannels, # 这里的num_inchannels=stage2_cfg[c]
num_modules, num_branches, num_blocks, num_channels, block, fuse_method,
multi_scale_output=True): # 同时layer_config=stage2_cfg 所以inchannels==channels
num_modules = num_modules # layer_config['NUM_MODULES']#[1, 1, 4, 3]
num_branches = num_branches # layer_config['NUM_BRANCHES']#[1, 2, 3, 4]#每个stage 分支数
num_blocks = num_blocks # layer_config['NUM_BLOCKS']#[[4], [4, 4], [4, 4, 4], [4, 4, 4, 4]]
num_channels = num_channels # layer_config['NUM_CHANNELS']#[[64], [48, 96], [48, 96, 192], [48, 96, 192, 384]]#各条分支的通道数
block = block # blocks_dict[layer_config['BLOCK']]#Bottleneck,BasicBlock
fuse_method = fuse_method # layer_config['FUSE_METHOD']#'sum'
# 总结就是 (一条分支 4个重复的Bottleneck) 重复1次 module1
# + (两条分支 4个重复的BasicBlock) 重复1次 module2
# + (三条分支 4个重复的BasicBlock) 重复4次 module3
# + (四条分支 4个重复的BasicBlock) 重复3次 module4
modules = []
for i in range(num_modules): # stage2 重复1次
# multi_scale_output is only used last module 只在一个module[i]的第4次重复用
if not multi_scale_output and i == num_modules - 1:
reset_multi_scale_output = False
else: # 当i == num_modules - 1 且 multi_scale_output==true时
reset_multi_scale_output = True
modules.append(
HighResolutionModule(num_branches, # 2
block, # BasicBlock
num_blocks, # [4,4]
num_inchannels, # [48,96]
num_channels, # [48,96]
fuse_method, # 'sum'
reset_multi_scale_output) # 前三次重复False 第四次重复True
)
num_inchannels = modules[-1].get_num_inchannels()
return nn.Sequential(*modules), num_inchannels
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)#[1, 64, 128, 128]
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x)#[1, 64, 64, 64]
x = self.bn2(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.layer1(x)#[1, 256, 64, 64]
x_list = []#[1, 48, 64, 64] || [1, 96, 32, 32]
for i in range(self.num_branches[1]): # self.stage2_cfg['NUM_BRANCHES']
if self.transition1[i] is not None:
x_list.append(self.transition1[i](x))
else:
x_list.append(x)
y_list = self.stage2(x_list)#[1, 48, 64, 64] || [1, 96, 32, 32]
x_list = []
for i in range(self.num_branches[2]): # self.stage3_cfg['NUM_BRANCHES']
if self.transition2[i] is not None:
if i < self.num_branches[2]-1:
x_list.append(self.transition2[i](y_list[i]))
else:
x_list.append(self.transition2[i](y_list[-1]))
else:
x_list.append(y_list[i])
y_list = self.stage3(x_list)
x_list = []
for i in range(self.num_branches[3]): # self.stage4_cfg['NUM_BRANCHES']
if self.transition3[i] is not None:
if i < self.num_branches[3]-1:
x_list.append(self.transition3[i](y_list[i]))
else:
x_list.append(self.transition3[i](y_list[-1]))
else:
x_list.append(y_list[i])
x = self.stage4(x_list)
# Upsampling
x0_h, x0_w = x[0].size(2), x[0].size(3)
x1 = F.interpolate(x[1], size=(x0_h, x0_w),
mode='bilinear', align_corners=ALIGN_CORNERS) # , align_corners=ALIGN_CORNERS)#"nearest"'bilinear'
x2 = F.interpolate(x[2], size=(x0_h, x0_w),
mode='bilinear', align_corners=ALIGN_CORNERS) # , align_corners=ALIGN_CORNERS)
x3 = F.interpolate(x[3], size=(x0_h, x0_w),
mode='bilinear', align_corners=ALIGN_CORNERS) # , align_corners=ALIGN_CORNERS)
feats = torch.cat([x[0], x1, x2, x3], 1)
out_aux_seg = []
# ocr
out_aux = self.aux_head(feats)
# compute contrast feature
feats = self.conv3x3_ocr(feats)
context = self.ocr_gather_head(feats, out_aux)
feats = self.ocr_distri_head(feats, context)
out = self.cls_head(feats)
out_aux_seg.append(out_aux)
out_aux_seg.append(out)
return out_aux_seg
def init_weights(self, pretrained='', ):
logger.info('=> init weights from normal distribution')
for name, m in self.named_modules():
if any(part in name for part in {'cls', 'aux', 'ocr'}):
# print('skipped', name)
continue
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
elif isinstance(m, BatchNorm2d_class):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
if os.path.isfile(pretrained):
pretrained_dict = torch.load(pretrained, map_location={'cuda:0': 'cpu'})
logger.info('=> loading pretrained model {}'.format(pretrained))
model_dict = self.state_dict()
pretrained_dict = {k.replace('last_layer', 'aux_head').replace('model.', ''): v for k, v in
pretrained_dict.items()}
print(set(model_dict) - set(pretrained_dict))
print(set(pretrained_dict) - set(model_dict))
pretrained_dict = {k: v for k, v in pretrained_dict.items()
if k in model_dict.keys()}
# for k, _ in pretrained_dict.items():
# logger.info(
# '=> loading {} pretrained model {}'.format(k, pretrained))
model_dict.update(pretrained_dict)
self.load_state_dict(model_dict)
elif pretrained:
raise RuntimeError('No such file {}'.format(pretrained))
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = torch.randn(1, 3, 256, 256)
model = HighResolutionNet(hp.blocks, hp.num_channels, hp.num_modules, hp.num_branches, hp.num_blocks, hp.fuse_method)
output = model.forward(img)
print(output.shape)